Dietary Cholesterol is seen in all animal products such as meats, dairy products and eggs, deep fried items, processed food and some of the bakery products containing trans fats and saturated fats. Cholesterol is made in the liver and is essential to build up cell membranes, formation of sex hormones and form bile acid which help in digestion of fats.
Diabetes has long been considered a risk factor for developing a heart disease. The risk is approximately 2 to 4 times more than those without diabetes getting a heart disease. 65% of the deaths among those with diabetes are related to heart diseases. However, even among those with diabetes, the risk varies among individuals and is influenced by gender, duration of diabetes , presence of raised blood pressure, poor cholesterol control and smoking history. The elder the patient, the higher is the risk for developing a heart disease. Among the fairer sex, the protective effect of estrogen can prevent a heart disease till they stop menstruating. Having a higher body mass and high uric acid levels are also known to trigger heart diseases.
Though maintaining normal or near normal sugar levels can improve the outcome of diabetes in general, good control prevents the progression of or delays the onset of microvascular complications such as the eye, kidney and nerve damage ( retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy). However, tight control of the blood pressure and cholesterol levels are important in preventing the progression to or delay the onset of developing macrovascular complications such as stroke, blood vessel diseases of the legs and heart attacks.
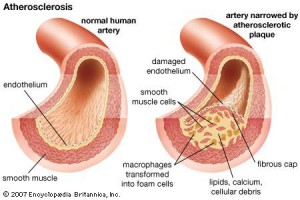
The cholesterol panel ( Lipid profile) is generally done after a 12 hour fasting. The blood is collected and the total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, ratio of cholesterol to HDL and LDL to HDL cholesterol is measured. The HDL cholesterol is the good cholesterol. The ratios mentioned above indicate the tendency to develop a block in the blood vessel. Cholesterol can get deposited in the inner linings of the blood vessels causing varying degrees of blocks. The blood vessel involvement is diffuse among those with diabetes and it has also been shown that numbers of collateral blood vessels are reduced among those with diabetes. The plaque which consists of the cholesterol deposit, can get dislodged and travel in the blood causing blocks elsewhere from its origin. Having pre diabetes, especially the increased glucose levels after meals only ( called IGT) is also a risk for developing a heart disease.
Better investigative modalities and better awareness among the people have helped improve the outcome, but because of sedentary lifestyle and enhanced use of junk food, high cholesterol levels and even heart attacks are quite common among the young.
But, when levels of cholesterol are high, it can get deposited in walls of arteries( blood vessels carrying blood from heart) . Normal levels < 5.2 mmol/L
HDL C ( High density lipoprotein cholesterol) is called the good cholesterol. This transports cholesterol from the blood and artery walls to the liver where it gets converted to bile which help in digestion of fats. Risk of coronary heart disease increases by 2-3% for every 1.0 mmol/L fall in levels of HDL C. Normal level > 1.0 mmol/L.
LDL C ( Low density Lipoprotein cholesterol) is called the bad cholesterol. This helps to transport cholesterol to various body cells and deposit the excess in walls of the arteries. Normal levels < 1.7 mmol/L if diabetic or < 2.3 mmol/L if not diabetic.
The cholesterol can get deposited on the inner linings of the blood vessels causing blocks in the eyes, heart supplying blood vessels, brain and kidneys causing blindness, heart attacks, strokes or paralysis, erectile dysfunction among males and kidney failure.
According to the data available with the various governing bodies around the globe, for every 10 mg/dL or 0.25 mmol/L increase of HDL, the good cholesterol, the risk for developing a heart attack is reduced by 2-3%. Similarly for every 1 mmol/L or 88.7 mg/dL increase of triglyceride level, the risk of developing a heart disease increases by 30% among men and 75% among women.
The main cholesterol level to be kept under control is the LDL cholesterol. The lower the level of LDL, less is the risk to develop a heart attack. Similarly, higher the HDL, the protective cholesterol, better is the outcome.
Non pharmacological ways to improve the HDL levels and reduce the LDL levels:
• Exercise
• Reduce smoking
• Increased consumption of avocados, a handful of non roasted non salted dry nuts( walnuts, almonds, pistachios).
• Olive oil or canola oil to be taken
• Reduction or avoiding red meat ( mutton, beef, pork, organ meat such as liver, gizzard)
• Reduction of deep fried food items
• Reduced intake of prawns, crabs and lobster.
• Reduced intake of full cream dairy products
When to treat with medicines?
When lifestyle modification and diet control alone do not help in lowering the levels, one will have to reconsider options of pharmacotherapy.
Guidelines from around the world have stressed the need for treatment with medicines in the following groups of people:
• If aged between 40-75 years with >7.5% risk of developing a heart attack in the next ten years
• If aged < 40 years with LDL cholesterol levels >190 mg/dL
• If person has suffered from any of the following:
• Heart attack
• Stroke or paralysis
• Transient ischemic attack ( features of stroke which reversed due to incomplete block to blood flow to brain)
• Those with peripheral artery disease of the extremities
• Those who have undergone revascularization procedures to improve blood flow in either heart or extremities
The risk for developing a heart attack is estimated by the health care professionals by using calculators incorporating ones race, gender, age, total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, blood pressure, use of medicines for controlling blood pressure, smoking and diabetes mellitus.
Normally the lipid profile ,which tests the various cholesterol types, is done after a 12 hour fasting. There are tests also which are available to assess how much of cholesterol has already lined the vessels. ( coronary angiogram, coronary calcium scoring and carotid doppler) Check the lipid levels once in 3 months if the levels are high or else once in 6 months. The doctor will advise when to start the medicines and if needed, when to stop the medicines. Some of the tests done to check heart functioning will also indirectly determine the lining of the vessels supplying the heart.( ECHO cardiogram and Stress Treadmill testing)
Statins, fibrates and drugs which reduce absorption of cholesterol from the intestines,ezetimibe, are used in treatment of high lipid levels. The former group is generally used around the world. Niacin is still being used in some parts of the world
A note on statins
Statins are generally found to have some side effects such as muscle pain and altered liver enzyme levels. It has also been associated with a 0.5% increase in chance in developing diabetes which led to a scare among the patients and health care providers.
However, statins have benefits besides lowering cholesterol levels, statins also help in stabilizing the plaque formation , reducing the inflammation of the blood vessels and regression of blocks to an extent. The plaque which is a mixture of calcium, lipids,fats and blood elements can get “fractured” and can shower small blocks through the blood vessels which can cause block at distant sites.
The benefits of taking a medicine to lower cholesterol far outweigh the risks associated with the medicine.
The benefits of taking medicines to control cholesterol go along way beyond just control of high levels. Cholesterol deposition almost always occurs in the inner lining of the blood vessels. People of some races are more prone for developing heart attacks when compared to people of other races. Some people inquire if they can stop the medicines for cholesterol once the levels are normal. Being a diabetic, the chances of getting a heart attack are high and so taking this tablet will go a long way to prevent the onset of developing a serious heart disorder. If intolerant to statins, there are other classes of medicines which can be used to control the cholesterol levels.
Some of the commonly used statins are Simvastatin, Fluvastatin, Atorvatstain and Rosuvastatin.
The dose needed depends on the treating health care professional and the need for starting the treatment as to whether it was for prevention or for treatment. If high doses are needed, the side effects can be minimized by addition of ezetimibe ( drug to impair absorption of cholesterol from intestines) or fibrates.
The liver enzyme levels and muscle enzyme level are checked frequently after starting therapy. A baseline level of the above enzymes are taken in some centers before commencing therapy.
The triglyceride levels are high among the Asians and South Indians due to their dietary habits and genetic make up. However among those in the rest of the world, LDL levels are high and targeted for control.
Exercise and impact on cholesterol
Link between coronary heart disease and cholesterol levels are well established through various studies.
Sedentary lifestyle adds to the risk for development of heart problems.
It has been shown by various studies that men who exercised more 75% of the maximum heart rate ( 220-age in years) at least 3 times a week for 12 weeks have reduced risk for developing heart disease. However, such studies have not been done on women.
In post menopausal women benefits of exercise were seen among those who exercise for 70% maximum heart rate for 24 weeks and who were on hormone replacement therapy. It was shown low to moderately intense exercise among post menopausal women improved outcomes.
The intensity, duration and frequency of exercise, the initial HDL C levels and length of the training period determine the benefits of exercise on cholesterol levels.
Exercising regularly for 8 months or jogging for 6 months or 3 weeks of diet control or brisk walking for three months can help reduce the LDL cholesterol. 5-10% body weight reduction can reduce the cholesterol levels. Recommendation is 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 1000 Kcals to be burned per week.
Omega 3 capsules taken once daily( containing fish oil) help to reduce a triglyceride levels to an extent. For the vegetarians, flaxseeds can be taken in place of Omega 3 capsules. There are no studies establishing the benefits of taking this to prevent heart attacks or strokes.
The diet should contain- 50-60% of total calories as carbohydrates, < 30% as fats, 15% as proteins, < 10% as polyunsaturated, < 20% as monounsaturated and 20-30 g of dietary fiber.
A note on oils.
Replacing saturated and transfats with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids can help improve the cholesterol levels.
If monounsaturated acids are used, there is a 12% reduction in total cholesterol and 15% reduction in LDL cholesterol. If polyunsaturated acids are used, cholesterol reduction by 19% and LDL by 22% is observed in studies.
Monounsaturated fatty acids are always better than polyunsaturated oils.
Remember that any oil when it is boiled loses its good properties. Hence, even olive oil or canola oil will not do any good if they are boiled.
Olive oil comes as extra virgin type and Pomace type. The extra virgin is used for raw consumption and the pomace type for cooking. Olive oil is actually the juice of olives unlike most of the oils made from the seeds.